Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium is the main element of this type of battery, since lithium ions are carried from cathode to anode (charging) through a separator and vice versa (discharging). Lithium-Ion (Li-Ion) batteries can be split into different types based on the other elements, mainly corresponding to the cathode’s chemical composition.
| Chemical Name | Material | Abbreviation | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium Cobalt Oxide | LiCoO2 | LCO | Cell phones, laptops, cameras |
| Lithium Manganese Oxide | LiMn2O4 | LMO | Power tools, EVs, medical, hobbyist |
| Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide | LiNiMnCo02 | NMC | Power tools, EVs, medical, hobbyist |
| Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide | LiNiCoAlO2 | NCA | EVs, grid storage |
| Lithium Iron Phosphate | LiFePO4 | LFP | Power tools, EVs, medical, hobbyist |
| Lithium Titanate Oxide | Li4Ti5O12 | LTO | EVs, grid storage |
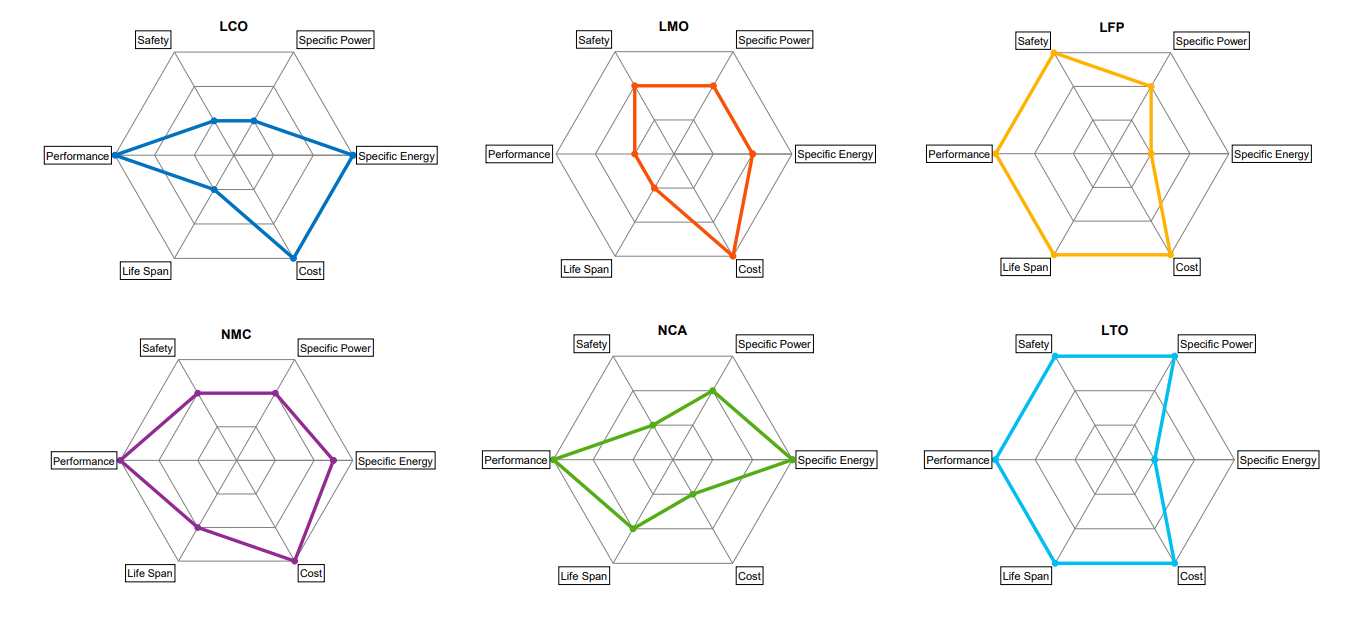
Each different type has different advantages, such as:
-
- LCO has an important specific energy;
- LMO has a high specific power;
- NCA and NMC are the cheapest Li-Ion batteries and the most stable from a thermal standpoint;
- LFP has a flat OCV curve but low capacity and high self-discharging rate; and
- LTO has a long lifespan and fast charge
Chemistry Comparison
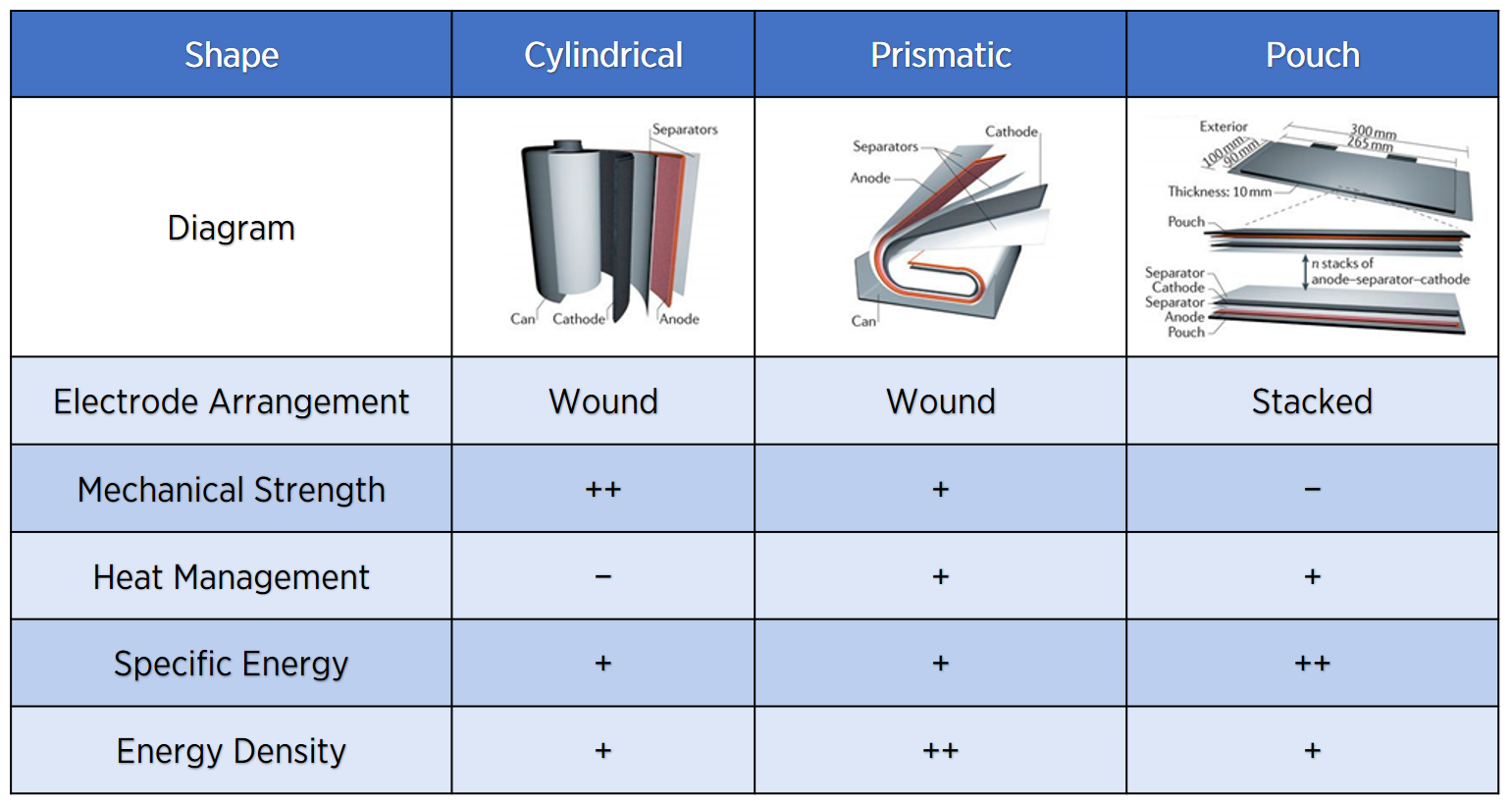
Physical Arrangement
Metal-Air Batteries
Metal-Air batteries combine the design features of both conventional batteries and fuel cells. They have large theoretical energy density (about 3~30 times higher than Lithium-Ion batteries) and are assembled from a metal anode and an air-breathing cathode with a proper electrolyte.
Currently it is still difficult to utilise Metal-Air batteries for land-based automotive use. However, we are always reviewing our selected technologies with a view to exploit new market opportunities, improve operating efficiencies and economies of scale.
| Metal–air battery | Energy, Wh/kg (including oxygen) |
Energy, Wh/kg (excluding oxygen) |
Open-Circuit Voltage, OCV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminium–air | 4300 | 8140 | 1.2 |
| Germanium–air | 1480 | 7850 | 1 |
| Calcium–air | 2990 | 4180 | 3.12 |
| Iron–air | 1431 | 2044 | 1.3 |
| Lithium–air | 5210 | 11140 | 2.91 |
| Magnesium–air | 2789 | 6462 | 2.93 |
| Potassium–air | 935 | 1700 | 2.48 |
| Sodium–air | 1677 | 2260 | 2.3 |
| Silicon–air | 4217 | 9036 | 1.6 |
| Tin–air at 1000 K | 860 | 6250 | 0.95 |
| Zinc–air | 1090 | 1350 | 1.65 |